Audiological Services
Pure Tone Audiometry
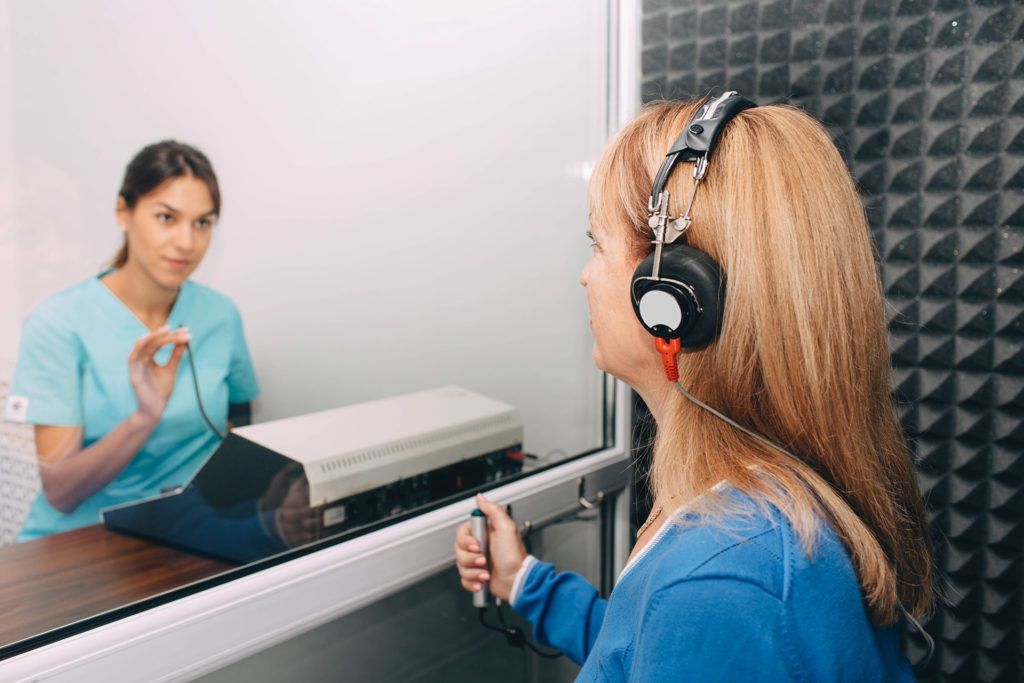

Pure tone audiometry is a basic and a very common diagnostic test that measures your hearing sensitivity to various frequencies (pitches) and intensities (loudness levels) of sounds in a sound proof room and performed by an Audiologist.
Pure tone audiometry is a basic and a very common diagnostic test that measures your hearing sensitivity to various frequencies (pitches) and intensities (loudness levels) of sounds in a sound proof room and performed by an Audiologist.
Here’s a brief overview of these services
What it is: Comprehensive hearing assessment using calibrated tones to measure hearing thresholds at different frequencies.
How it works: The individual responds to various tones, producing an audiogram illustrating their hearing levels, aiding in diagnosing hearing impairments.
When to use: Essential for diagnosing hearing loss, determining its extent, and planning appropriate interventions based on the audiogram results.
Impedance Audiometry
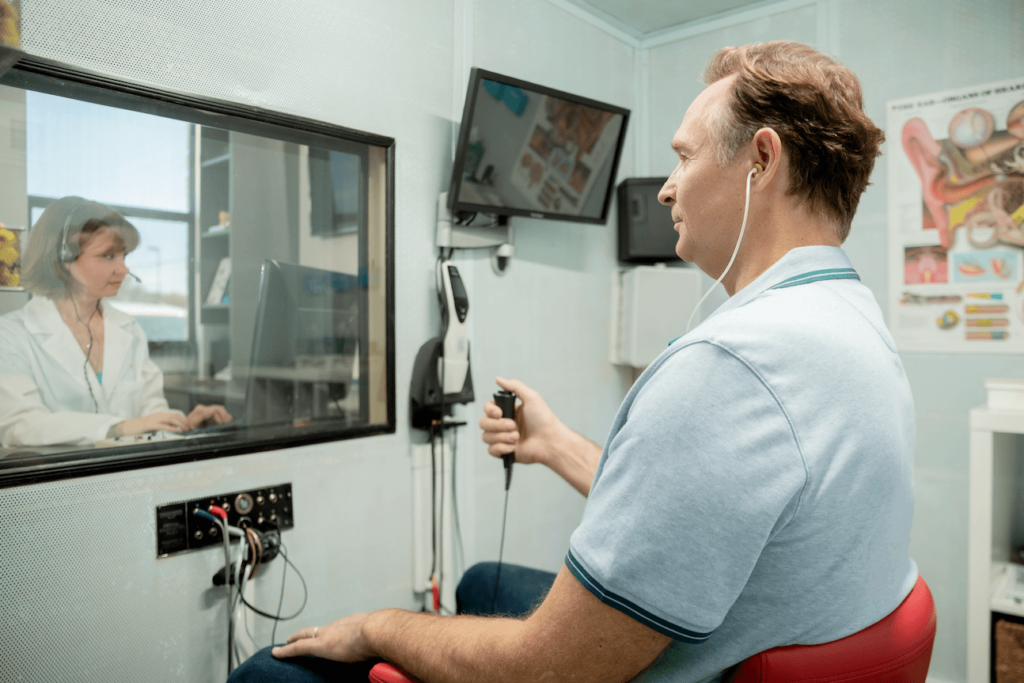

Evaluates middle ear function by measuring impedance changes, in
What it is: Visual reinforcement audiometry is a pediatric hearing test that employs visual cues to reinforce a child’s response to auditory stimuli. When the child responds to the sound, a visual reinforcement (such as a lighted toy) is presented, encouraging the child’s participation.
What it is: Measures middle ear function by assessing eardrum movement and involuntary muscle responses to sound.
How it works: Tympanometry evaluates middle ear pressure, while acoustic reflex testing examines muscle reflexes, assisting in diagnosing middle ear disorders.
When to use: Useful for diagnosing conditions like otitis media, providing insights into middle ear health, and guiding suitable treatment.
What it is: Evaluates the Eustachian tube’s ability to equalize middle ear pressure during swallowing.
How it works: Measures pressure changes in the middle ear, aiding in diagnosing Eustachian tube dysfunction and related issues.
When to use: Valuable for identifying problems like barotrauma, aiding in treatment planning for conditions affecting middle ear pressure.
What it is: Measures the sustainability of the acoustic reflex, indicating neural hearing disorders.
How it works: Evaluates the duration the acoustic reflex can be maintained, providing insights into auditory nerve function.
When to use: Beneficial for diagnosing neural hearing impairments, guiding appropriate interventions and management strategies.
Specialized Audiological Tests (for Vertigo related issues and others)
Specialized tests like SISI and TDT are often employed when standard audiometric evaluations do not provide sufficient information or when specific abnormalities need to be investigated in detail.
Here’s a brief overview of these services
What it is: Measures sensitivity to small changes in sound intensity.
How it works: Assesses the ability to detect slight volume variations, aiding in the diagnosis of auditory processing disorders.
When to use: Useful for identifying auditory processing issues, guiding tailored interventions for individuals with difficulty processing subtle sound changes.
What it is: Measures the duration a tone can be heard, providing insights into auditory processing.
How it works: Evaluates sustained perception of a tone, aiding in diagnosing auditory processing disorders.
When to use: Beneficial for understanding auditory processing difficulties, guiding suitable interventions and therapies for improved auditory perception.